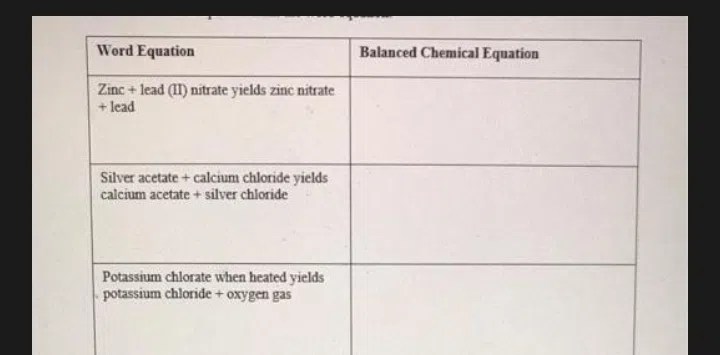
Zinc lead ii nitrate yield zinc nitrate lead – Delving into the intriguing realm of zinc lead II nitrate yield, this exploration unravels the intricate chemical reaction between zinc, lead(II) nitrate, and zinc nitrate, delving into the factors that influence yield and showcasing the diverse applications of zinc nitrate across various industries.
Chemical Reaction
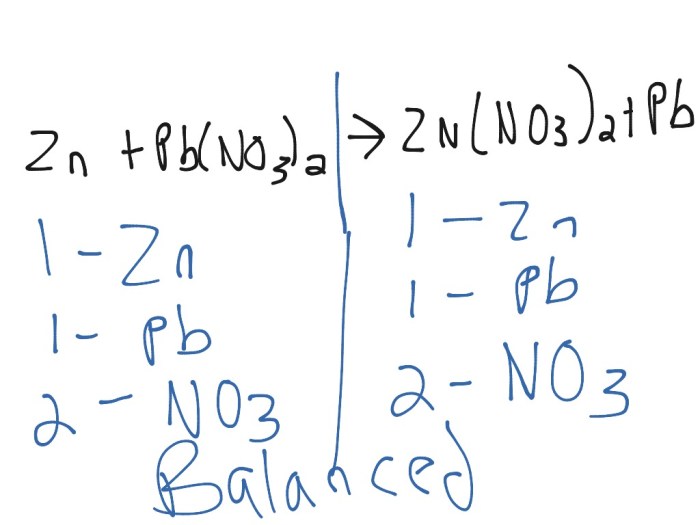
The chemical reaction between zinc, lead(II) nitrate, and zinc nitrate can be represented by the following balanced equation:
Zn + Pb(NO3) 2→ Zn(NO 3) 2+ Pb
This reaction is a single-displacement reaction, where zinc displaces lead from lead(II) nitrate.
Yield of Zinc Nitrate
The theoretical yield of zinc nitrate can be calculated using the mole ratio from the balanced chemical equation and the given masses of the reactants. Assuming we have 1 mole of zinc and 1 mole of lead(II) nitrate, the theoretical yield of zinc nitrate would be 1 mole.
However, the actual yield may be lower than the theoretical yield due to factors such as incomplete reaction, loss of product during purification, and side reactions.
To improve the yield, one can use excess zinc or lead(II) nitrate, ensure complete mixing of the reactants, and optimize the reaction conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure).
Properties of Zinc Nitrate
Zinc nitrate is a colorless, crystalline solid with the formula Zn(NO 3) 2. It is soluble in water and has a melting point of 36.4 °C and a boiling point of 136 °C.
Zinc nitrate is a strong oxidizing agent and can react violently with reducing agents. It is also corrosive to metals and can cause skin irritation.
Applications of Zinc Nitrate
Zinc nitrate has a variety of applications, including:
- As a fertilizer for plants
- As a mordant in dyeing
- As a wood preservative
- As an analytical reagent
Safety Considerations, Zinc lead ii nitrate yield zinc nitrate lead
Zinc nitrate is a hazardous substance and should be handled with care. It is important to wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and eye protection, when working with zinc nitrate.
Zinc nitrate should be stored in a cool, dry place away from incompatible materials, such as reducing agents and flammable materials.
Zinc nitrate can have a negative environmental impact if released into the environment. It is important to dispose of zinc nitrate properly according to local regulations.
Questions Often Asked: Zinc Lead Ii Nitrate Yield Zinc Nitrate Lead
What is the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between zinc, lead(II) nitrate, and zinc nitrate?
Zn + Pb(NO3)2 → Zn(NO3)2 + Pb
What factors can affect the actual yield of zinc nitrate?
Purity of reactants, reaction temperature, reaction time, and side reactions
What are some applications of zinc nitrate in different industries?
Fertilizer, mordant, wood preservative, analytical chemistry