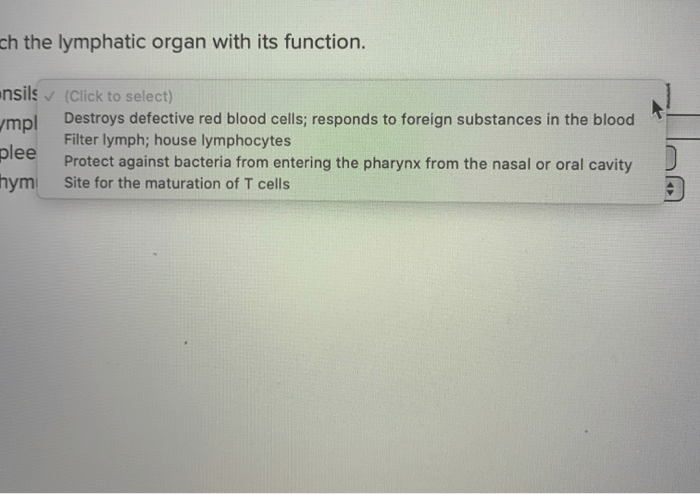
Match the lymphoid organ with its description, embarking on a journey to unravel the intricate tapestry of our immune system’s sentinels. From the thymus, the cradle of T cells, to the spleen, the vigilant filter of our bloodstream, each lymphoid organ plays a vital role in safeguarding our health.
Join us as we delve into their unique structures, locations, and functions, unraveling the secrets of our body’s remarkable defense mechanisms.
Lymphoid Organs
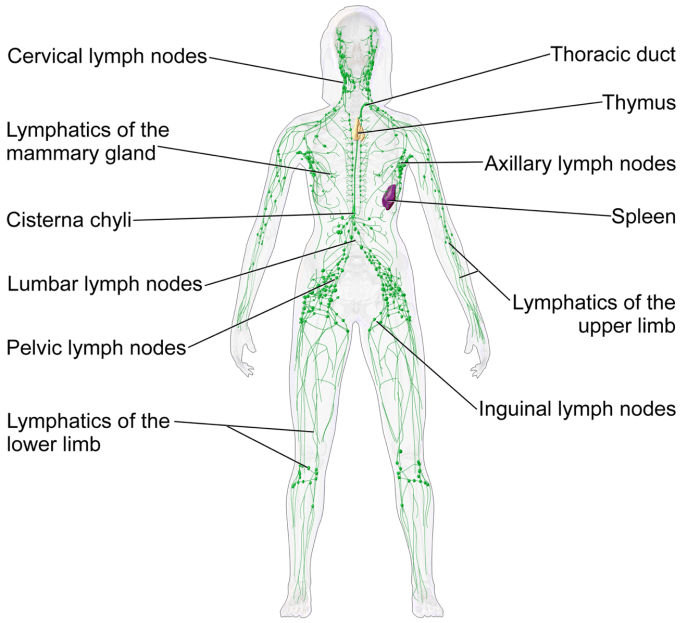
Lymphoid organs are specialized structures in the body that play a crucial role in the immune system. They serve as sites for the development, maturation, and activation of immune cells, which are essential for protecting the body against pathogens and maintaining overall health.
The major lymphoid organs include:
- Thymus
- Spleen
- Lymph nodes
- Tonsils
- Peyer’s patches
- Appendix
- Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
Thymus
The thymus is a bilobed organ located in the upper chest cavity, behind the sternum. It is responsible for the maturation and development of T cells, a type of white blood cell that plays a critical role in cell-mediated immunity.
Spleen
The spleen is a large, bean-shaped organ located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It filters blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells and other cellular debris. The spleen also serves as a reservoir for immune cells and plays a role in immune responses.
Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures located throughout the body. They filter lymph fluid, removing pathogens and debris. Lymph nodes also contain immune cells that can recognize and respond to antigens, initiating an immune response.
Tonsils
Tonsils are small, lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. They play a role in the immune defense of the upper respiratory tract, trapping and filtering pathogens that enter through the mouth or nose.
Peyer’s Patches
Peyer’s patches are lymphoid tissues located in the small intestine. They are responsible for the immune defense of the gastrointestinal tract, protecting against pathogens that enter through food or drink.
Appendix
The appendix is a small, finger-shaped structure attached to the large intestine. Its exact role in the immune system is still not fully understood, but it is thought to play a role in immune responses and may contain beneficial bacteria.
Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT), Match the lymphoid organ with its description
MALT is a network of lymphoid tissues located in the mucosal membranes of the body, including the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital tracts. MALT plays a crucial role in the immune defense of mucosal surfaces, protecting against pathogens that enter through these routes.
Expert Answers: Match The Lymphoid Organ With Its Description
What is the primary function of lymphoid organs?
Lymphoid organs serve as strategic hubs for immune cell development, maturation, and activation, orchestrating the body’s defense against pathogens and foreign invaders.
Why is the thymus crucial for the immune system?
The thymus acts as a training ground for T cells, equipping them with the ability to recognize and eliminate harmful invaders while maintaining tolerance to self-tissues.
How does the spleen contribute to immune defense?
The spleen acts as a filter, removing pathogens and damaged red blood cells from the bloodstream, while also serving as a reservoir for immune cells.