Embarking on a journey through the realm of mathematics, we present the Quadratic Relations and Conic Sections Unit Test, an in-depth exploration of these fundamental concepts. Delve into the intricacies of parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, and circles, unraveling their equations, graphs, and real-world applications.
This comprehensive guide equips you with a thorough understanding of quadratic relations, empowering you to solve equations with ease and confidence. Master the art of graphing conic sections, discerning their key features and characteristics. Prepare yourself for the unit test with practice problems, effective study techniques, and expert insights.
Quadratic Relations and Conic Sections: Quadratic Relations And Conic Sections Unit Test
Quadratic relations and conic sections are fundamental concepts in mathematics that have wide-ranging applications in various fields. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these topics, covering their definitions, properties, and applications.
Understanding Quadratic Relations
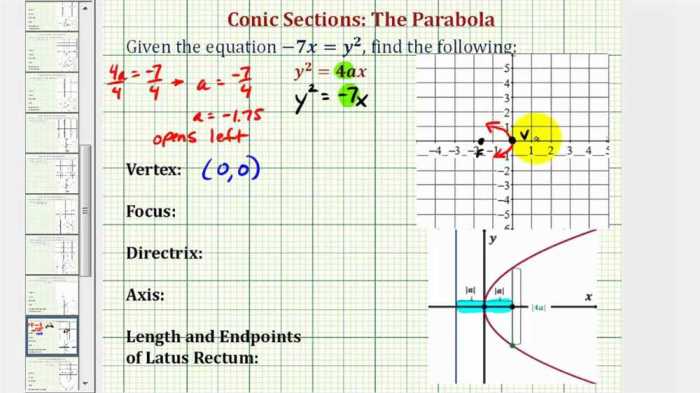
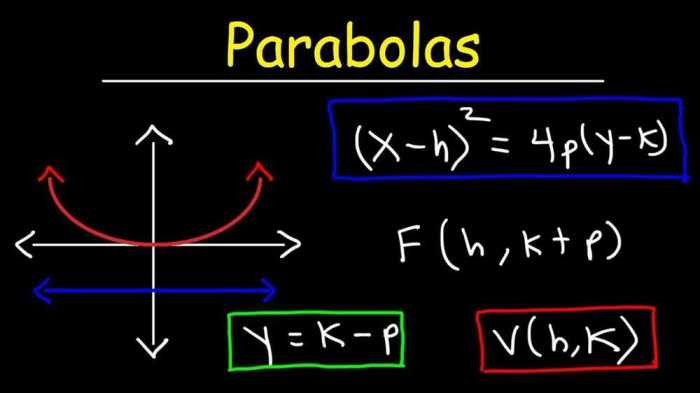
A quadratic relation is an equation of the form ax 2+ bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. The graph of a quadratic relation is a parabola, a U-shaped curve.
The vertex of a parabola is the point where it changes direction, and the axis of symmetry is the vertical line passing through the vertex. The intercepts of a parabola are the points where it intersects the x-axis.
Solving Quadratic Equations, Quadratic relations and conic sections unit test
There are several methods for solving quadratic equations, including factoring, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula. Factoring involves finding two numbers that multiply to give c and add to give b. Completing the square involves adding and subtracting a constant to the equation to create a perfect square trinomial.
The quadratic formula is a general formula that can be used to solve any quadratic equation.
Graphing Conic Sections
Conic sections are curves that are formed by intersecting a plane with a cone. There are four types of conic sections: parabolas, circles, ellipses, and hyperbolas. Each type of conic section has its own unique equation and graph.
- Parabolas:y = ax 2+ bx + c
- Circles:(x – h) 2+ (y – k) 2= r 2
- Ellipses:(x – h) 2/a 2+ (y – k) 2/b 2= 1
- Hyperbolas:(x – h) 2/a 2– (y – k) 2/b 2= 1
Applications of Quadratic Relations and Conic Sections
Quadratic relations and conic sections have numerous applications in real-world problems. Quadratic relations can be used to model projectile motion, optimization problems, and other situations where the relationship between two variables is quadratic. Conic sections are used in modeling planetary orbits, sound waves, and other phenomena.
Test Preparation Strategies
To prepare for a unit test on quadratic relations and conic sections, students should review the key concepts and formulas related to these topics. They should also practice solving quadratic equations and graphing conic sections. Effective study techniques include spaced repetition, active recall, and using practice problems and solutions.
Helpful Answers
What is the significance of the discriminant in solving quadratic equations?
The discriminant determines the nature of the solutions to a quadratic equation. A positive discriminant indicates two distinct real solutions, a zero discriminant indicates one real solution (a double root), and a negative discriminant indicates no real solutions (complex solutions).
How do I determine the center of a conic section from its equation?
For a parabola, the center is given by the vertex (h, k). For a circle, the center is given by (h, k). For an ellipse, the center is given by ((h, k). For a hyperbola, the center is given by (h, k).
What are some real-world applications of quadratic relations?
Quadratic relations are used in modeling projectile motion, optimization problems, and the design of parabolic structures such as bridges and arches.