The rock pocket mouse activity answer key unravels the fascinating intricacies of these elusive creatures, revealing their nocturnal rhythms, habitat preferences, and remarkable adaptations. This comprehensive guide delves into the secret lives of rock pocket mice, shedding light on their unique behaviors and the factors that shape their existence.
From their distinctive activity patterns to their specialized diets and intricate social structures, this answer key provides a comprehensive understanding of these enigmatic animals. Prepare to embark on a journey of discovery as we uncover the secrets of the rock pocket mouse.
Rock Pocket Mouse Activity Patterns: Rock Pocket Mouse Activity Answer Key
Rock pocket mice are primarily nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night. During the day, they typically rest in burrows or crevices to avoid predators and conserve energy. As the sun sets, they emerge from their shelters and engage in various activities, including foraging for food, exploring their surroundings, and interacting with conspecifics.
The specific timing of their activity patterns can vary depending on several factors, including season, temperature, and food availability. During the summer months, when temperatures are high, they may be more active at dusk and dawn to avoid the heat of the day.
In the winter, when food resources are scarce, they may extend their activity periods to increase their chances of finding sustenance.
Habitat Preferences and Range
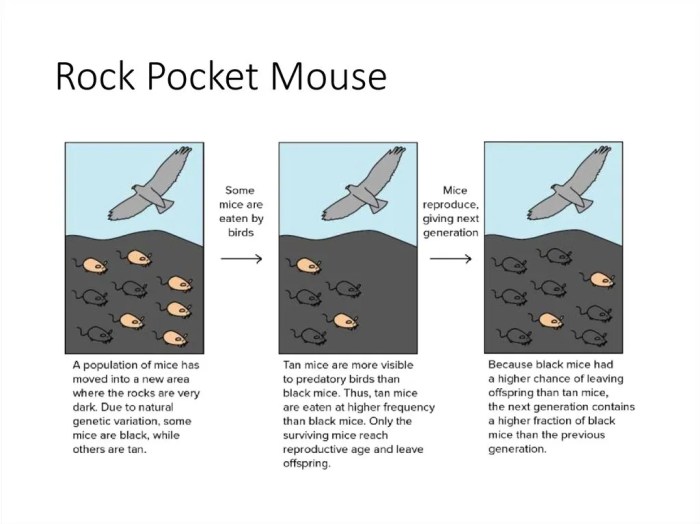
Rock pocket mice are found in rocky habitats, particularly in areas with abundant crevices and boulders that provide shelter and protection from predators. They prefer dry, well-drained areas with sparse vegetation, such as deserts, scrublands, and rocky outcrops.
The geographic range of rock pocket mice extends across the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. They are found in states such as Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, Utah, and California, as well as in the Mexican states of Sonora and Chihuahua.
The distribution of rock pocket mice is influenced by factors such as vegetation, topography, and climate. They are more likely to be found in areas with abundant rock cover and sparse vegetation, as these habitats provide the necessary shelter and foraging opportunities.
Additionally, they prefer areas with mild temperatures and low precipitation, as extreme weather conditions can be detrimental to their survival.
Diet and Foraging Behavior
Rock pocket mice are omnivorous, with a diet that consists primarily of seeds, insects, and plant material. They are opportunistic feeders and will consume a wide variety of food items, including fruits, nuts, leaves, and small invertebrates.
They typically forage on the ground, using their keen sense of smell to locate food. They may also climb rocks and vegetation to reach food sources that are out of reach. Their foraging strategies vary depending on the availability of food resources.
In areas with abundant food, they may engage in short, frequent foraging bouts. In areas with scarce food, they may travel longer distances and spend more time foraging.
Rock pocket mice have several adaptations that enable them to exploit their specific food resources. Their cheek pouches allow them to store food for later consumption, which is particularly useful when food is scarce. Additionally, their strong teeth and powerful jaws enable them to crack open hard seeds and nuts.
Social Behavior and Communication
Rock pocket mice are generally solitary animals, except during the breeding season. They maintain individual territories that they defend against conspecifics. However, they may interact with each other in various social contexts, such as mating, territorial disputes, and resource sharing.
Rock pocket mice communicate using a variety of vocalizations, scent marking, and body language. They emit high-pitched calls to attract mates, defend their territories, and communicate with their young. They also use scent marking to establish their territories and communicate with other individuals.
These communication methods play a vital role in the social interactions and survival of rock pocket mice. They allow them to establish and maintain their territories, attract mates, and coordinate their activities.
Physiological Adaptations

Rock pocket mice have several physiological adaptations that enable them to survive in their harsh and arid environment. These adaptations include efficient thermoregulatory mechanisms, water conservation strategies, and other specialized features related to their habitat.
Rock pocket mice have a high surface-area-to-volume ratio, which allows them to dissipate heat effectively. They also have the ability to enter a state of torpor, which is a period of reduced metabolic activity, during the hottest hours of the day.
This adaptation helps them to conserve energy and water.
Additionally, rock pocket mice have specialized kidneys that allow them to conserve water. They can produce highly concentrated urine, which reduces water loss. They also have the ability to absorb water from their food and from the air.
These physiological adaptations are essential for the survival of rock pocket mice in their arid and rocky habitat. They allow them to regulate their body temperature, conserve water, and withstand the harsh conditions of their environment.
FAQ Summary
What are the primary food sources of rock pocket mice?
Seeds, insects, and plant matter
How do rock pocket mice communicate with each other?
Vocalizations, scent marking, and body language
What factors influence the habitat selection of rock pocket mice?
Vegetation, topography, and climate