Welcome to the realm of food webs and energy pyramids, where we embark on an enlightening journey to decipher the intricate tapestry of life within ecosystems. Food webs and energy pyramids worksheet answers are our guide, illuminating the fundamental principles that govern the flow of energy and matter through ecological communities.
As we delve into the complexities of food webs, we unravel the interconnectedness of species, tracing the intricate pathways of energy transfer from producers to consumers. Energy pyramids, on the other hand, provide a visual representation of the hierarchical distribution of energy within ecosystems, highlighting the crucial role of each trophic level.
Definition and Overview of Food Webs
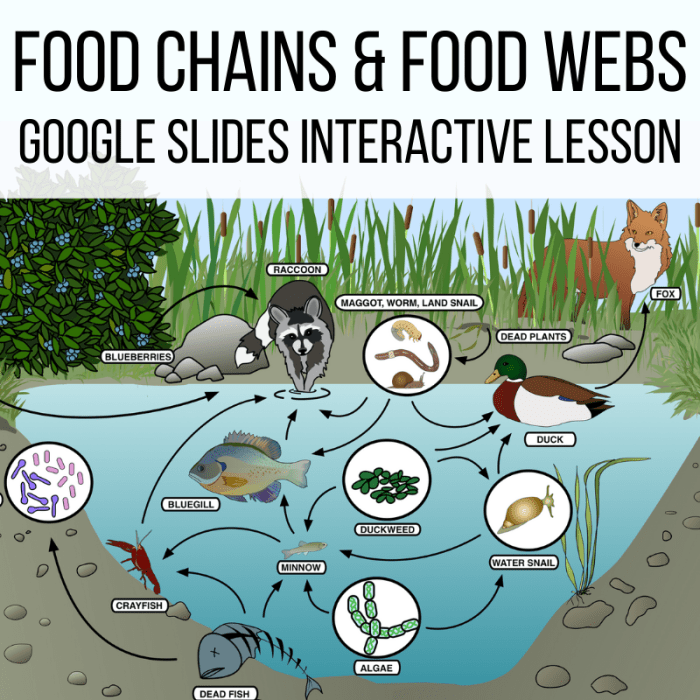
Food webs are complex networks of interconnected food chains that describe the feeding relationships between organisms within an ecosystem. They provide a comprehensive representation of the flow of energy and nutrients through different trophic levels, helping us understand the ecological dynamics and stability of various habitats.
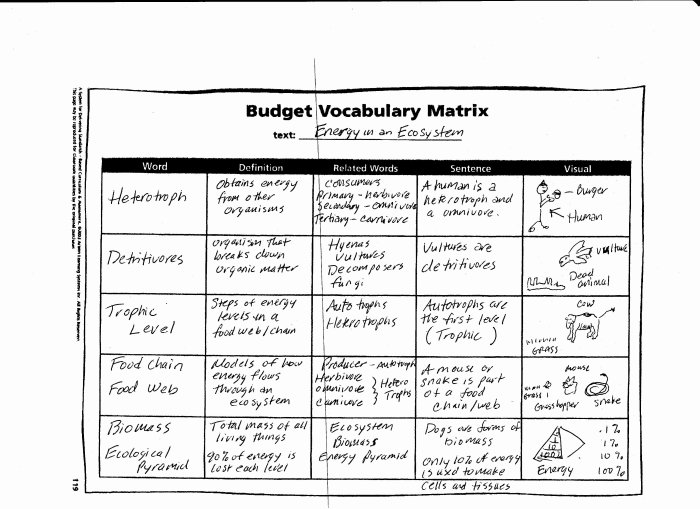
Trophic levels refer to the position of organisms in a food web based on their feeding habits. Primary producers, such as plants and algae, form the base of the food web by capturing energy from sunlight through photosynthesis. Primary consumers, typically herbivores, feed on primary producers.
Secondary consumers, usually carnivores, feed on primary consumers. Tertiary consumers, often apex predators, occupy the highest trophic level by consuming secondary consumers. Energy flows unidirectionally through these trophic levels, with each level transferring approximately 10% of its energy to the next higher level.
Construction of Food Webs
Constructing a food web involves identifying the different organisms in an ecosystem and mapping their feeding relationships. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify and list all the organisms present in the ecosystem.
- Determine the feeding habits of each organism based on observations, literature, or expert knowledge.
- Draw arrows to represent the flow of energy from one organism to another, starting with primary producers.
- Connect organisms that share a predator-prey relationship.
- Label each trophic level and indicate the direction of energy flow.
Tips for identifying organisms and their relationships:
- Observe feeding behaviors directly or through field studies.
- Consult scientific literature and databases for information on species’ diets.
- Seek expert advice from ecologists or biologists familiar with the ecosystem.
Analysis of Food Webs
Analyzing food webs provides insights into the health and resilience of ecosystems. Common metrics used include:
Connectance
Connectance measures the proportion of possible feeding links that are actually present in a food web. A highly connected food web indicates a diverse and stable ecosystem, as multiple pathways exist for energy flow.
Stability
Stability refers to the ability of a food web to resist disturbances and maintain its structure and function. Factors influencing stability include species diversity, redundancy (multiple species performing similar roles), and the presence of keystone species (species with a disproportionate impact on the ecosystem).
Energy Pyramids
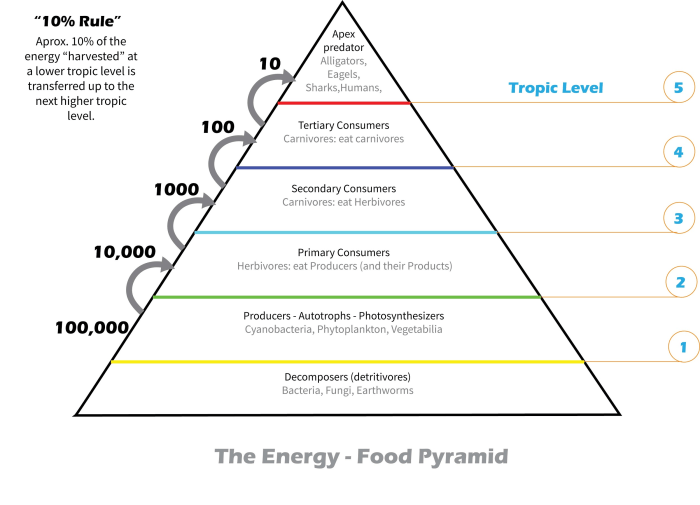
Energy pyramids graphically represent the flow of energy through different trophic levels. They are typically triangular in shape, with the base representing the primary producers and the apex representing the apex predators. Each level of the pyramid represents a specific trophic level, with the width of each level proportional to the amount of energy available at that level.
Energy pyramids demonstrate the loss of energy as it moves up the food chain. At each trophic level, approximately 90% of the energy is lost as heat, metabolic processes, or waste. This energy loss limits the number of trophic levels that can be supported in an ecosystem.
Applications of Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Food webs and energy pyramids are valuable tools in various fields:
Conservation Biology, Food webs and energy pyramids worksheet answers
Understanding food webs helps identify keystone species, which play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance. Conservation efforts can focus on protecting these species to ensure the stability of the entire ecosystem.
Ecosystem Management
Food webs and energy pyramids inform ecosystem management practices. By understanding the flow of energy and nutrients, managers can make informed decisions about resource allocation, habitat restoration, and invasive species control.
Commonly Asked Questions: Food Webs And Energy Pyramids Worksheet Answers
What is a food web?
A food web is a graphical representation of the feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem, illustrating the complex interconnectedness of species.
What is an energy pyramid?
An energy pyramid is a diagram that depicts the amount of energy available at each trophic level within an ecosystem, showcasing the loss of energy as it flows through the food chain.
Why are food webs and energy pyramids important?
Food webs and energy pyramids provide valuable insights into the structure and functioning of ecosystems, enabling ecologists to assess the health and resilience of these intricate natural communities.