Classify each element as a metal nonmetal or semimetal – Classify each element as a metal, nonmetal, or semimetal sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of element classification, providing a clear understanding of the properties and characteristics that define each category.
The periodic table serves as the foundation for our exploration, with its organization providing a systematic framework for understanding the behavior and relationships between elements. As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the unique characteristics of metals, nonmetals, and semimetals, examining their physical and chemical properties, and exploring the similarities and differences that shape their classification.
Periodic Table Organization
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It is generally accepted that the modern periodic table was first published by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, although several other scientists had developed similar tables prior to this.The
periodic table is divided into 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. The groups are numbered 1-18 from left to right, and the periods are numbered 1-7 from top to bottom. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties, while elements in the same period have similar atomic structures.The
periodic table is a powerful tool for organizing and understanding the chemical elements. It can be used to predict the properties of an element based on its position in the table, and it can also be used to identify trends in chemical behavior.
Classification of Elements
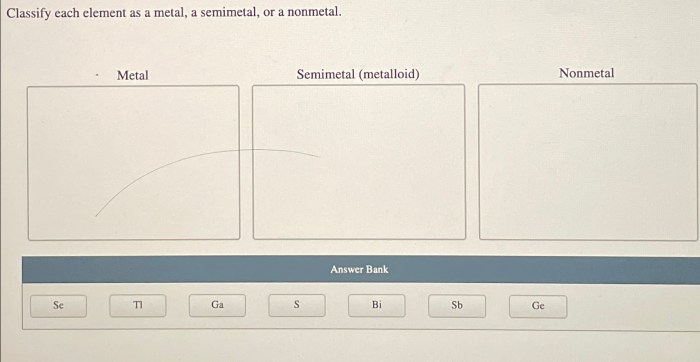
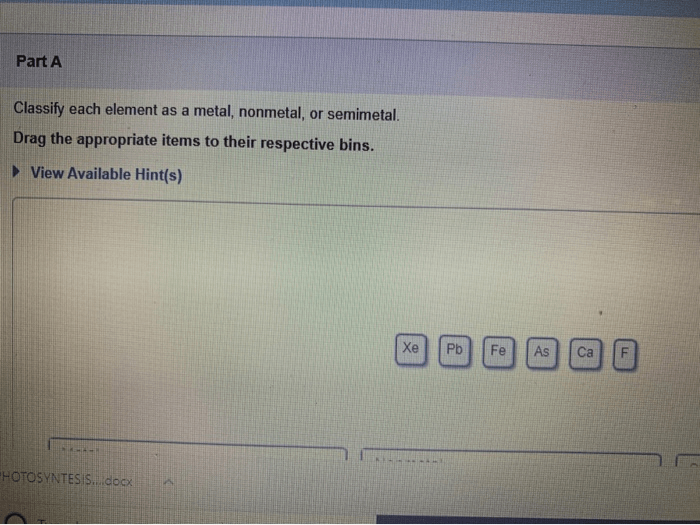
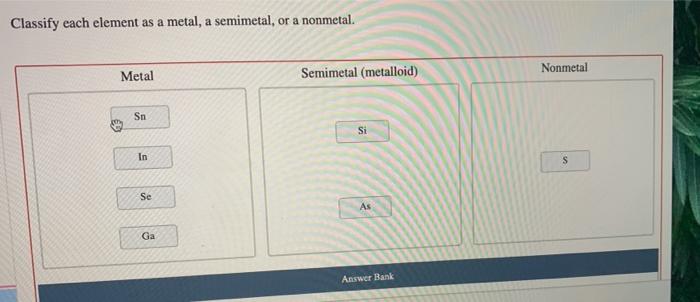
Elements can be classified into three main categories: metals, nonmetals, and semimetals. Metals are characterized by their high electrical and thermal conductivity, their malleability and ductility, and their shiny appearance. Nonmetals, on the other hand, are characterized by their low electrical and thermal conductivity, their brittleness, and their dull appearance.
Semimetals, also known as metalloids, have properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals.The classification of elements into metals, nonmetals, and semimetals is based on their electronic structures. Metals have one or more valence electrons, which are electrons in the outermost energy level of the atom.
These valence electrons are loosely bound to the atom, and they can easily move from one atom to another. This mobility of valence electrons is what gives metals their high electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as their malleability and ductility.Nonmetals,
on the other hand, have few or no valence electrons. This means that their valence electrons are tightly bound to the atom, and they cannot easily move from one atom to another. This lack of mobility of valence electrons is what gives nonmetals their low electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as their brittleness.Semimetals
have a number of valence electrons that is intermediate between that of metals and nonmetals. This gives them properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. For example, semimetals have electrical and thermal conductivities that are lower than those of metals but higher than those of nonmetals.
They are also more brittle than metals but less brittle than nonmetals.
Examples of Metals
| Element | Symbol | Physical Appearance | Conductivity | Malleability | Ductility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Cu | Shiny, reddish-brown | High | Yes | Yes |
| Iron | Fe | Shiny, silvery-gray | High | Yes | Yes |
| Aluminum | Al | Shiny, silvery-white | High | Yes | Yes |
| Gold | Au | Shiny, yellow | High | Yes | Yes |
| Silver | Ag | Shiny, white | High | Yes | Yes |
Examples of Nonmetals
| Element | Symbol | Physical Appearance | Conductivity | Reactivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | O | Colorless gas | Low | High |
| Nitrogen | N | Colorless gas | Low | Low |
| Carbon | C | Solid (graphite, diamond) | Low | Varies |
| Chlorine | Cl | Yellow-green gas | Low | High |
| Sulfur | S | Yellow solid | Low | High |
Examples of Semimetals
| Element | Symbol | Physical Appearance | Conductivity | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boron | B | Black solid | Semiconductor | Semiconductors, nuclear reactors |
| Silicon | Si | Gray solid | Semiconductor | Semiconductors, solar cells |
| Germanium | Ge | Gray solid | Semiconductor | Transistors, photodiodes |
| Arsenic | As | Gray solid | Semiconductor | Semiconductors, lasers |
| Antimony | Sb | Gray solid | Semiconductor | Semiconductors, flame retardants |
Borderline Cases
There are a few elements that exhibit characteristics of multiple categories. For example, beryllium is a metal that is also somewhat brittle, which is a characteristic of nonmetals. Another example is tellurium, which is a semimetal that is also somewhat reactive, which is a characteristic of nonmetals.The
classification of these borderline cases can be challenging. However, it is generally agreed that the element should be classified into the category that it most closely resembles. For example, beryllium is classified as a metal because it has more characteristics of a metal than a nonmetal.
Similarly, tellurium is classified as a semimetal because it has more characteristics of a semimetal than a nonmetal.
Applications of Element Classification, Classify each element as a metal nonmetal or semimetal
The classification of elements is a powerful tool that has a wide range of applications in material science, chemistry, and other fields. For example, the classification of elements can be used to:* Predict the properties of new materials
- Design new materials with specific properties
- Understand the chemical reactions that occur between different elements
- Develop new technologies that use elements in new ways
The classification of elements is a fundamental part of chemistry, and it is a tool that is used by scientists and engineers every day.
Q&A: Classify Each Element As A Metal Nonmetal Or Semimetal
What is the significance of the periodic table in classifying elements?
The periodic table provides a systematic arrangement of elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. This organization allows us to identify patterns and trends in element behavior, making it a powerful tool for classifying and understanding the properties of different elements.
How do the physical properties of metals differ from those of nonmetals?
Metals are typically shiny, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals, on the other hand, are often dull, brittle, and poor conductors. These contrasting physical properties reflect the differences in their atomic structures and bonding characteristics.
What are some examples of semimetals and how are they used?
Semimetals, such as silicon and germanium, possess properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals. They are semiconductors, meaning their electrical conductivity can be controlled by manipulating their atomic structure. This property makes semimetals essential components in electronic devices, including transistors, solar cells, and computer chips.